
Azure Landing Zone (workload migration)
Azure Landing Zone is a foundational concept in Azure cloud migration that provides a structure for designing and deploying Azure workloads. It involves a set of best practices, guidelines, and templates that help you establish a standard approach for migrating and managing workloads in Azure. In this blog, we'll discuss Azure Landing Zone in detail and how it can help organizations streamline their workload migration to Azure.
What is Azure Landing Zone?
Azure Landing Zone is a cloud adoption framework that provides a standardized approach for deploying Azure resources. It consists of a set of pre-built templates, policies, and governance controls that enable organizations to establish a secure and scalable foundation in Azure. The Azure Landing Zone approach allows organizations to migrate their workloads to Azure with minimal disruption while ensuring compliance and security.
The Azure Landing Zone approach is based on four key pillars:
Governance: The governance pillar establishes a framework for managing Azure resources, including policies, guidelines, and processes to ensure compliance and security. This pillar enables organizations to maintain consistent governance across all their Azure subscriptions and enforce regulatory compliance requirements.
Network: The network pillar provides the foundation for designing and deploying networking infrastructure in Azure. It includes virtual networks, subnets, routing, and security controls that allow organizations to establish secure connectivity between their on-premises environment and Azure.
Identity and access management: The identity and access management (IAM) pillar provides a framework for managing user identities and permissions in Azure. It includes role-based access control (RBAC) policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and Azure Active Directory (AD) integration that enable organizations to manage access to their Azure resources.
Operations: The operations pillar provides a framework for managing Azure resources and workloads. It includes monitoring, logging, backup and disaster recovery, and automation tools that enable organizations to operate their workloads in Azure effectively.
Benefits of Azure Landing Zone
The Azure Landing Zone approach provides several benefits for organizations looking to migrate their workloads to Azure, including:
Standardization: Azure Landing Zone provides a standard approach to deploying Azure resources, enabling organizations to establish a consistent deployment model across all their Azure subscriptions.
Governance: Azure Landing Zone enables organizations to enforce governance controls, policies, and compliance requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Security: Azure Landing Zone provides a secure foundation for deploying Azure resources, including network security, IAM, and compliance controls that help organizations to protect their data.
Scalability: Azure Landing Zone enables organizations to scale their Azure resources and workloads in a consistent and repeatable manner, reducing the time and effort required to deploy new resources.
Steps for deploying an Azure Landing Zone:
Define your requirements: The first step in deploying an Azure Landing Zone is to define your requirements. This includes understanding your organization's compliance and security requirements, as well as your networking and identity and access management requirements.
Choose your deployment method: There are several deployment methods for deploying an Azure Landing Zone, including Azure Portal, Azure CLI, and ARM templates. Choose the method that best fits your needs.
Design your architecture: Once you've defined your requirements and chosen your deployment method, you'll need to design your Azure Landing Zone architecture. This will include defining your virtual networks, subnets, and security controls, as well as your IAM policies and monitoring and logging requirements.
Deploy your Azure Landing Zone: Once your architecture is defined, you can deploy your Azure Landing Zone using your chosen deployment method. This will include deploying your virtual networks, subnets, and security controls, as well as configuring your IAM policies and monitoring and logging tools.
Test and validate: Once your Azure Landing Zone is deployed, you'll need to test and validate it to ensure it meets your requirements. This will include testing your networking and security controls, as well as your IAM policies and monitoring and logging tools.
Iterate and optimize: Once your Azure Landing Zone is validated, you can begin iterating and optimizing it based on your organization's evolving needs. This will include adding new resources, updating your policies, and refining your architecture
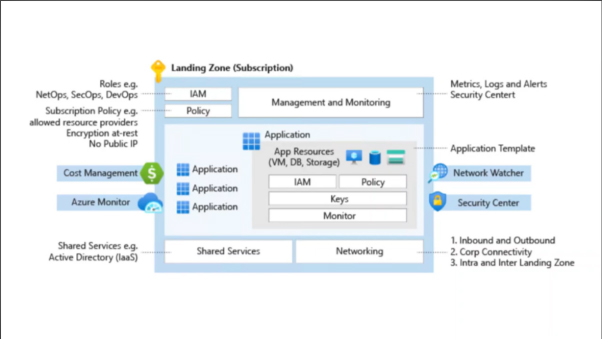
The architecture of an Azure Landing Zone typically includes the following components:
Management Group Hierarchy: A management group hierarchy is a collection of management groups that are used to organize Azure resources. Each management group represents a level in the hierarchy, and you can apply policies and governance controls at each level.
Subscription: A subscription is a logical container for Azure resources, and it provides a secure and dedicated space for deploying workloads. Each subscription is associated with a billing account and can have its own set of policies and governance controls.
Resource Groups: Resource groups are logical containers for Azure resources that enable you to manage resources at a more granular level. Each resource group can contain resources from different services and can be used to apply policies and governance controls.
Virtual Networks: Virtual networks enable you to create isolated network environments in Azure. You can create multiple subnets within a virtual network, and you can use network security groups (NSGs) to apply security controls at the subnet level.
Identity and Access Management: Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is used to manage user identities and permissions in Azure. You can use role-based access control (RBAC) policies to assign permissions to users and groups, and you can use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to provide an additional layer of security.
Monitoring and Logging: Azure provides a set of tools for monitoring and logging your Azure resources, including Azure Monitor and Azure Log Analytics. These tools enable you to monitor performance, detect and diagnose issues, and analyze usage and performance data.
Automation: Azure provides a set of automation tools, including Azure Automation, Azure Functions, and Azure Logic Apps. These tools enable you to automate repetitive tasks and workflows, and to orchestrate complex processes.
The architecture of an Azure Landing Zone is designed to provide a secure and scalable foundation for deploying workloads in Azure. By leveraging the components described above, you can establish a consistent deployment model and governance framework, and ensure compliance and security across all your Azure resources.
Conclusion
Azure Landing Zone provides a standardized approach for designing and deploying Azure resources, enabling organizations to streamline their workload migration to Azure while ensuring compliance and security. The approach provides a foundation for managing Azure resources, including governance, network, IAM, and operations. By deploying Azure Landing Zones, organizations can benefit from a standard deployment model, consistent governance, and a secure and scalable foundation for their Azure workloads.



